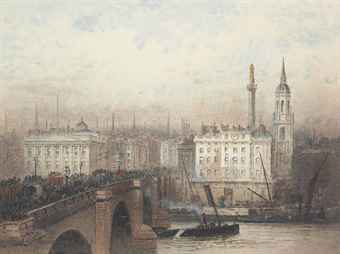
Today’s post is in honor of the late musicologist Karl Haas, host of Adventures in Good Music, the nationally syndicated radio program which aired between 1970 and 2007. The Story of the Bells, broadcast on Christmas Eve, was one of Haas’ most popular episodes. It provided listeners with a sample of the varied and distinctive sounds of bell ringing in cities throughout Europe and the Middle East.
Here at The Listeners’ Club, we’ve returned to bell ringing at Christmas. (Here are posts from last year and the year before). Continuing that tradition, let’s climb into the belfries of a few of Europe’s most famous churches for an up-close view:
Change Ringing at St. Magnus the Martyr
We’ll start with a spectacular example of change ringing from the Church of St. Magnus the Martyr in the center of London. This style of bell ringing, which emerged in England in the seventeenth century, requires great precision. Tuned bells are rung in a series of mathematical permutations which produce a set of patterns. As this documentary points out, ten bells could produce over three million unique combinations!
The Church of St. Magnus the Martyr was designed by Sir Christopher Wren (architect of London’s St. Paul’s Cathedral) and built between 1671 and 1687. A previous church on the location was destroyed by the Great Fire of 1666. As the historic view above shows, the church, along with neighboring spires and Nelson’s Column, once dominated the skyline. Now, the church is surrounded, and almost obscured, by anonymous office blocks constructed after the Blitz.
The Guild of St. Magnus rings the bells every Sunday around 12:15:
[hr]
A mist hung over the river, deepening the red glare of the fires that burnt upon the small craft moored off the different wharves, and rendering darker and more indistinct the murky buildings on the banks. The old smoke-stained storehouses on either side, rose heavy and dull from the dense mass of roofs and gables, and frowned sternly upon the water too black to reflect even their lumbering shapes. The tower of old Saint Saviour’s Church, and the spire of Saint Magnus, so long the giant-warders of the ancient bridge, were visible in the gloom; but the forest of shipping below the bridge, and the thickly scattered spires of churches above, were nearly all hidden from the sight.
-Charles Dickens, Oliver Twist
[hr]
Frankfurt Cathedral
For a comparison, here is what it’s like to stand in the belfry of Frankfurt Cathedral, home to Germany’s third largest bell ( weighing 11,950 kg. and sounding on the pitch, E). Each bell enters individually, adding up to a mighty chorus. As Karl Haas said, “a sound which leaves no room for human voices.”
Salzburg
Here are the nine bells of the Franciscan Church in Salzburg:
[hr]
…and bells remembered…
John Luther Adams’ 2005 composition, …and bells remembered…
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qlQjqdTF4z8



